key 属性与补丁渲染(基础虚拟 DOM 章节开始了)
重大问题
实际上,我们现在实现的 Chibivue 还存在一个非常严重的问题。
在之前实现 patch 补丁渲染程序的时候,
关于
patchChildren,需要通过添加key属性来处理动态大小的子元素。
你还记得这句话吗?
让我们看看实际发生了什么问题。
目前,我们的 patchChildren 方法的实现是这样的:
const patchChildren = (n1: VNode, n2: VNode, container: RendererElement) => {
const c1 = n1.children as VNode[]
const c2 = n2.children as VNode[]
for (let i = 0; i < c2.length; i++) {
const child = (c2[i] = normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
patch(c1[i], child, container)
}
}这基于 c2(即下一个 vnode)的数组长度进行循环的。 换句话说,它只在 c1 和 c2 基本相同时才起作用。
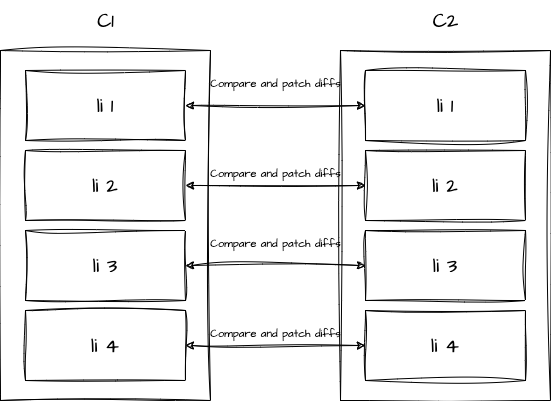
假如,我们现在是进行元素的删除。
那么由于 patch 是根据 c2 的进行遍历的,因此 c1 中的第四个元素将没有办法执行 patch。
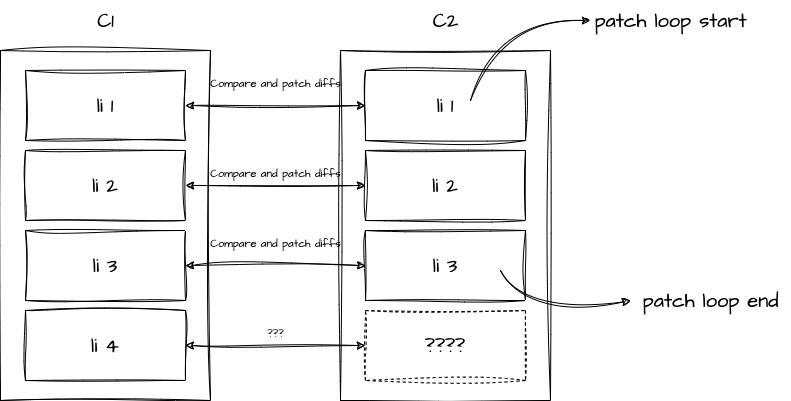
发生这种情况时,只会简单的对 1 ~ 3 这三个元素进行更新,c1 中的第四个元素不会消失,而是会被保留下来。
我们来看看他的实际效果:
import { createApp, h, reactive } from 'chibivue'
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ list: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] })
const updateList = () => {
state.list = ['e', 'f', 'g']
}
return () =>
h('div', { id: 'app' }, [
h(
'ul',
{},
state.list.map(item => h('li', {}, [item])),
),
h('button', { onClick: updateList }, ['update']),
])
},
})
app.mount('#app')当我们点击 update 按钮时,页面会变成这样。

虽然列表的前面三个元素已经正确更新为 ["e", "f", "g"],但是 d 依然还存在。
实际上,不仅仅是删除这种情况会出现问题。 当我们向其中插入新的元素时,由于是基于 c2 进行遍历更新的,所以会变成这样:
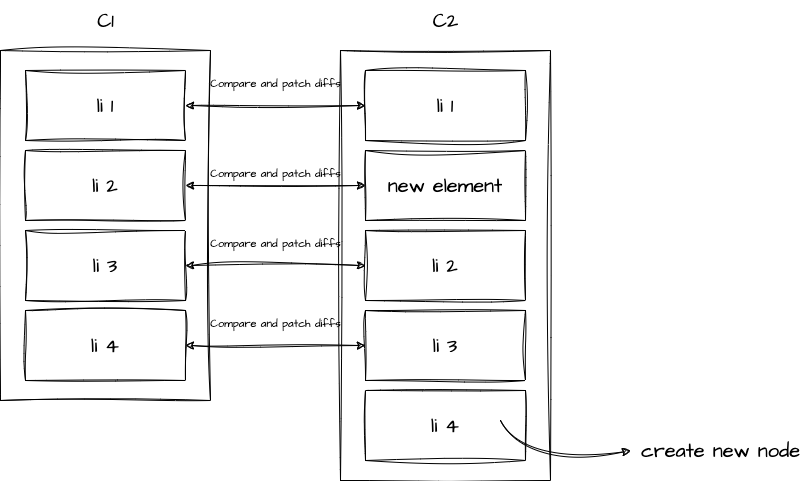
然而,我们实际插入的元素是 new element,我们希望的是比较 c1, c2 之间 li 1, li 2, li 3, li 4 四个元素前后分别发生了什么变化。
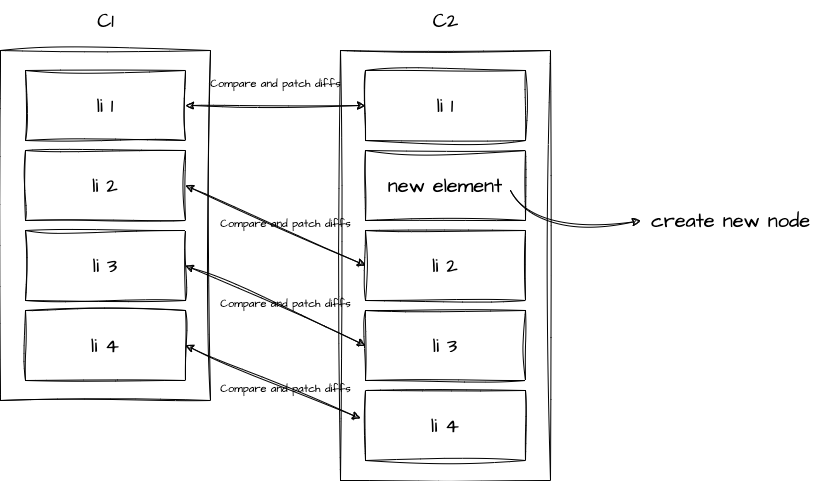
这两个问题的共同点在于,我们无法确定 c1 与 c2 中,哪些元素应该被视为同一节点。
为了解决这个问题,我们有必要在每个元素上添加一个 key 属性,然后在比较这个 key 的基础上进行补丁更新。
现在,我们来回顾一下 Vue 官方文档中对 key 的解释:
key这个特殊的attribute主要作为 Vue 的虚拟 DOM 算法提示,在比较新旧节点列表时用于识别vnode。
https://cn.vuejs.org/api/built-in-special-attributes.html#key
事实上,我们可能也听说过 “不要将 v-for 循环中的 index 作为 key”。但是在现在这种情况下,key 属性被隐式地设置为了 index。 这也就是为什么会出现这种问题(以 c2 的长度来进行 for 循环,以 index 为基准进行与 c1 中元素的 patch 对比更新)。
用 key 属性来实现 patch
这是由一个名为 patchKeyedChildren 的函数来实现的(让我们在 Vue 源码中找到它)。
方法是首先为所有新节点创建一个由节点 key 和节点下标 index 组成 Map 映射。
let i = 0
const l2 = c2.length
const e1 = c1.length - 1 // end index of prev node
const e2 = l2 - 1 // end index of next node
const s1 = i // start index of prev node
const s2 = i // start index of next node
const keyToNewIndexMap: Map<string | number | symbol, number> = new Map()
for (i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
const nextChild = (c2[i] = normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
if (nextChild.key != null) {
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i)
}
}在最初的 Vue 的源码中,这个 patchKeyedChildren 分为 5 个部分。
- sync from start
- sync from end
- common sequence + mount
- common sequence + unmount
- unknown sequence
然而,前面四个都只能算是最简单的情况,只有最后一个 unknown sequence 在功能实现上是最重要的。
但是,以上四个都是优化,因此在功能上只有最后一个“未知序列”可以工作。 因此,让我们直接从 unknown sequence 部分开始实现。
首先,我们先忽略元素移动的这种情况,只根据 key 完成 VNode 的 patch 更新。
利用我们刚刚创建的 keyToNewIndexMap,我们可以计算出 c1 与 c2 之间节点的对应关系并更新他们。 在这之后,你必须要处理剩下的新元素挂载或者旧元素的移除。
大概的意思就是这样了 ↓ (这里我省略了很多内容。详细信息大家可以阅读 vuejs/core 的 renderer.ts 部分的源代码。)
const toBePatched = e2 + 1
const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched) // 新 index 索引与旧 index 索引的映射
for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++) newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0
// 基于 e1 (旧元素数组的长度) 遍历
for (i = 0; i <= e1; i++) {
const prevChild = c1[i]
newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key)
if (newIndex === undefined) {
// 如果在 keyToNewIndexMap 找不到对应关系,说明需要卸载
unmount(prevChild)
} else {
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex] = i + 1 // 新旧索引对应关系
patch(prevChild, c2[newIndex] as VNode, container) // patch 对比更新
}
}
for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const nextIndex = i
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex] as VNode
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {
// 如果新旧索引映射数组中没有对应的旧节点索引(依旧是 newIndexToOldIndexMap 初始化时的状态(0))
// 则说明这是一个新元素,需要执行挂载(即实际上原来不存在这个节点)
patch(null, nextChild, container, anchor)
}
}移动元素
方法
Node.insertBefore
目前,我们根据 key 属性的匹配来完成了元素的更新,但是没有处理位置移动。 所以,我们现在还需要实现一个移动元素到指定位置的操作函数。
首先,我们来讨论一下如何移动元素。
我们在之前的 nodeOps 中实现的 insert 函数里定义了一个参数 anchor。 anchor 顾名思义,就是 “锚点” 的意思。 如果您查看我们在 runtime-dom 中编写的 insert 方法,可以看到它是用 insertBefore 方法实现的。
export const nodeOps: Omit<RendererOptions, 'patchProp'> = {
// .
// .
// .
insert: (child, parent, anchor) => {
parent.insertBefore(child, anchor || null)
},
}将锚点节点当做第二个参数传递给 insertBefore,则原节点会插入到锚点节点的前面。 https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Node/insertBefore
我们使用这个方法来实现 DOM 节点的实际移动
LIS (Longest Increasing Subsequence,最长递增子序列)
关于如何实现节点的移动算法,还是有点复杂的。
我们都知道 DOM 操作与运行 JS 计算相对性能消耗要昂贵得多,因此我们都希望能尽可能地减少移动次数,以便避免出现额外移动(多余移动操作)。
所以,我们使用所谓的 “最长递增子序列” 算法。顾名思义,就是找到数组中最长且逐步递增的子序列。
例如,当存在如下数组时:
[2, 4, 1, 7, 5, 6]它存在这样几个递增子序列。
[2, 4]
[2, 5]
.
.
[2, 4, 7]
[2, 4, 5]
.
.
[2, 4, 5, 6]
.
.
[1, 7]
.
.
[1, 5, 6]它们都是逐渐递增的序列,其中最长的序列就是 “最长递增子序列”。
换句话说,上面的 [2, 4, 5, 6] 就是最长的递增子序列,所以在 Vue 中,[2, 4, 5, 6] 对应的索引数组被视为计算结果(即 [0, 1, 4, 5])。
大家可以看一下这个示例函数:
function getSequence(arr: number[]): number[] {
const p = arr.slice()
const result = [0]
let i, j, u, v, c
const len = arr.length
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const arrI = arr[i]
if (arrI !== 0) {
j = result[result.length - 1]
if (arr[j] < arrI) {
p[i] = j
result.push(i)
continue
}
u = 0
v = result.length - 1
while (u < v) {
c = (u + v) >> 1
if (arr[result[c]] < arrI) {
u = c + 1
} else {
v = c
}
}
if (arrI < arr[result[u]]) {
if (u > 0) {
p[i] = result[u - 1]
}
result[u] = i
}
}
}
u = result.length
v = result[u - 1]
while (u-- > 0) {
result[u] = v
v = p[v]
}
return result
}我们将使用此函数从 newIndexToOldIndexMap 中计算出最长递增子序列,并在此基础上使用 insertBefore 插入其他节点。
具体示例
现在我们结合一个具体的示例,来让大家更好的理解。
假设现在我们有 c1 和 c2 两个 vnode 数组,其中 c1 对应更新前的状态,c2 对应更新后的状态。 每个一个 vnode 对象都有一个 key 属性(当然,实际上每个 vnode 对象还有其他信息)。
c1 = [{ key: 'a' }, { key: 'b' }, { key: 'c' }, { key: 'd' }]
c2 = [{ key: 'a' }, { key: 'b' }, { key: 'd' }, { key: 'c' }]在此基础上,我们生成一个 keyToNewIndexMap 对象(上文中有介绍,由 c2 中的 key 与 index 索引组成的 Map 对象)
※ 以下就是我们之前介绍过的代码。
const keyToNewIndexMap: Map<string | number | symbol, number> = new Map()
for (i = 0; i <= e2; i++) {
const nextChild = (c2[i] = normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
if (nextChild.key != null) {
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i)
}
}
// keyToNewIndexMap = { a: 0, b: 1, d: 2, c: 3 }接下来,我们生成 newIndexToOldIndexMap 对象。
※ 一样是上文介绍过的内容。
// 初始化
const toBePatched = c2.length
const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched) // 新索引与旧索引的映射
for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++) newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0
// newIndexToOldIndexMap = [0, 0, 0, 0]// 在 patch 执行时生成用于移动元素的 newIndexToOldIndexMap 对象
// 基于 e1 (旧vnode 数组的长度) 进行循环
for (i = 0; i <= e1; i++) {
const prevChild = c1[i]
newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key)
if (newIndex === undefined) {
// 在新 vnode 数组中找不到对应元素,则移除旧节点
unmount(prevChild)
} else {
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex] = i + 1 // 得到同一节点的新旧索引映射
patch(prevChild, c2[newIndex] as VNode, container) // 对比更新
}
}
// newIndexToOldIndexMap = [1, 2, 4, 3]然后,从生成的 newIndexToOldIndexMap 中获取到最长递增索引部分(这里是新添加的)
const increasingNewIndexSequence = getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap)
// increasingNewIndexSequence = [0, 1, 3]j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1
for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const nextIndex = i
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex] as VNode
// ※ 如果您可以将 parentAnchor 视为作为参数接收的锚点
const anchor = nextIndex + 1 < l2 ? (c2[nextIndex + 1] as VNode).el : parentAnchor
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {
// newIndexToOldIndexMap 的初始值为 0,所以如果为 0,则判定不存在到旧元素的映射,说明是新增元素。
patch(null, nextChild, container, anchor)
} else {
// 如果 i 和 increaseNewIndexSequence[j] 不匹配则说明需要移动
if (j < 0 || i !== increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {
move(nextChild, container, anchor)
} else {
j--
}
}
}实际实现一下吧。
现在,我们只是大概说了一下如何实现函数 patchKeyedChildren 的思路,现在我们尝试自己实现一下吧。
这里总结一下实现步骤:
- 允许透传
anchor参数 (在insert方法中可以用这个参数进行元素移动) - 以
c2为基础,准备key和index的映射对象map。 - 以上一步创建的
map对象,再次生成c2中的index与c1中对应元素的index的新旧索引对象。
在此阶段,需要基于c1和基于c2的循环(不包括move)中执行patch更新。 - 根据步骤 3 中得到的映射对象,找出最长递增子序列。
- 根据步骤 4 和
c2中获得的子序列执行move元素移动。
你可以参考 Vue.js 或者 Chibivue 的源代码实现来完成(我建议是在阅读 Vue.js 的源码的同时进行代码实现)。
 The chibivue Book
The chibivue Book